A rule aimed at shielding LGBT students from discrimination in educational settings is currently on hold in 26 states.
This regulation, essential for preventing discrimination based on gender identity, is in a state of limbo, waiting on the U.S. Supreme Court to decide if it can be implemented across these states.
Supreme Court’s Silence

The Biden administration’s efforts to get the Supreme Court to overturn lower court injunctions have not yet been addressed.
These injunctions keep the rule from being implemented in ten states led by Republican administrations, who argue against it, leaving the rule’s fate uncertain as the legal proceedings drag on.
Enforcement Is a Patchwork

Due to the ongoing legal disputes, the rule’s enforcement is inconsistent across the country.
The Education Department is currently able to apply this rule in only 24 of the 50 states. Introduced in April, it aims to extend the protections of Title IX, which traditionally bans sex discrimination in federally funded schools.
Education Department Holds Firm

“We will continue to fight for every student,” said a spokesperson from the Education Department.
This vow to uphold the April 2024 Title IX regulations highlights the department’s commitment to navigating through the legal hurdles to ensure that these protections are fully realized.
Broad Legal Challenges

The Biden administration is not standing down, seeking the Supreme Court’s guidance in lawsuits filed by several states including Louisiana, Mississippi, and Idaho, among others.
These states have brought forth significant legal opposition that the administration is now challenging at the highest level.
What Does Discrimination Mean Here?

At the center of the administration’s efforts is a push to clarify that discrimination “on the basis of sex” should explicitly include sexual orientation and gender identity.
This definition is crucial to the administration’s goal of ensuring educational fairness and preventing discrimination.
Resistance from States

The rule has been met with significant resistance.
Critics argue it mandates too much change too quickly, requiring schools to allow access to restrooms and locker rooms based on gender identity and compelling faculty to use students’ chosen pronouns, sparking a heated debate about the role of federal regulations in education.
Safety Concerns Take Center Stage
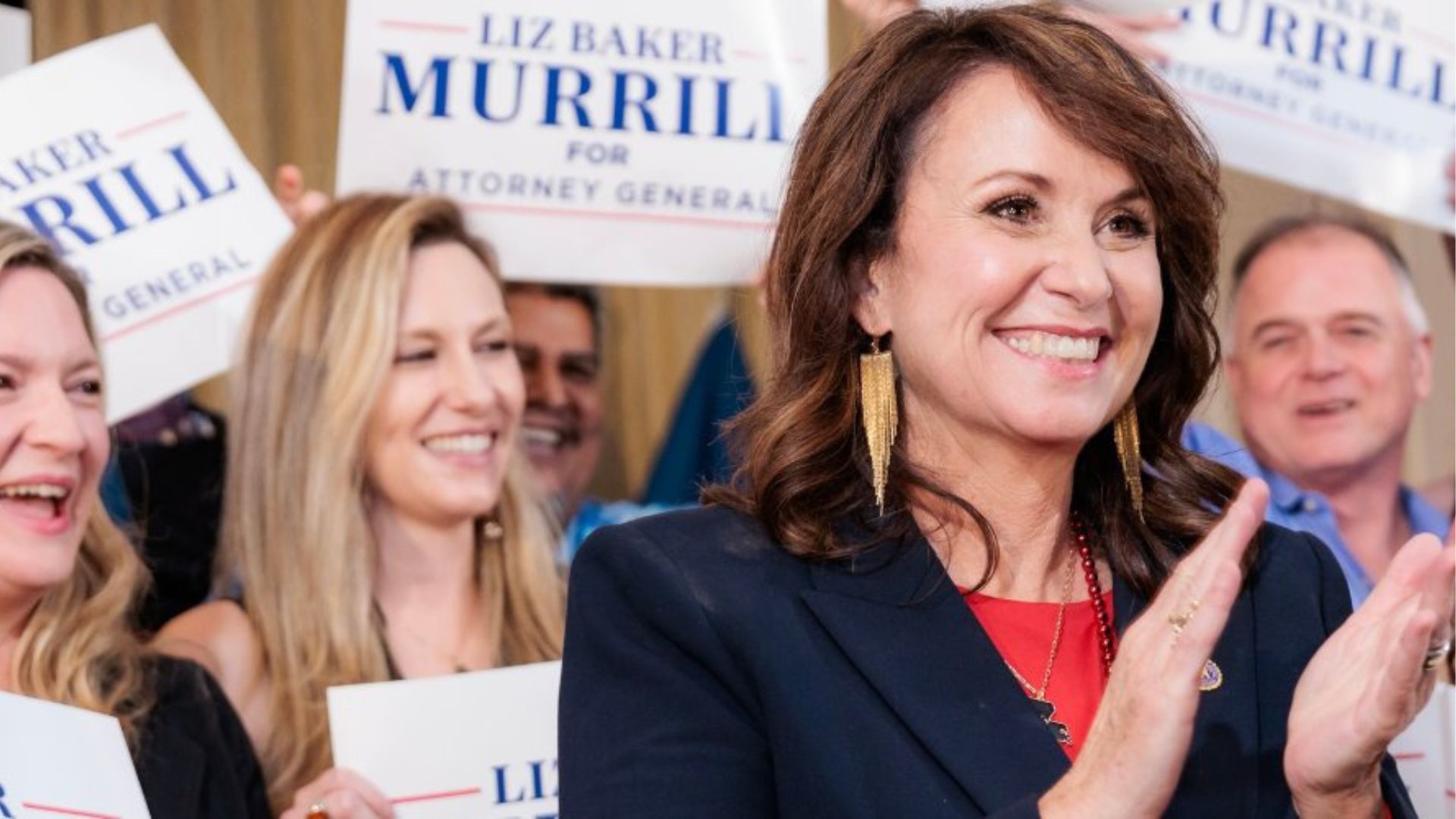

Louisiana Attorney General Liz Murrill expressed deep concerns, criticizing the rule for pursuing “a political agenda” at the expense of “significant safety concerns for young women” across educational institutions in Louisiana and nationwide.
Her remarks highlight the emotional and contentious nature of the debate, underscoring the divisive impact of the rule on communities and policymakers.
A Victory Short-lived
Despite the rule being temporarily upheld in states like Alabama and Florida, this relief was brief as the 11th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals quickly paused its enforcement.
This judicial back-and-forth demonstrates the ongoing uncertainty surrounding the rule’s future.
Beyond LGBT Issues

This rule doesn’t just seek to protect LGBT students.
It also aims to bolster protections for pregnant students, parents, and guardians, demonstrating a comprehensive approach to fighting discrimination in education under Title IX.
Tying Into Supreme Court Precedents

The administration argues that this rule is a natural extension of the Supreme Court’s 2020 decision, which recognized that laws against sex-based discrimination in the workplace also protect against discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity.
This precedent plays a key role in the current legal arguments for the rule.
Decisive Moments Ahead

The Supreme Court is poised to review key decisions by district judges who assert that Title IX’s protections are limited to “biological” sex.
The outcomes of these reviews will significantly influence the landscape of educational policy and the rights of transgender individuals across the U.S., setting the stage for landmark rulings on these crucial issues.
