Not everything is as it seems, especially concerning the world’s oldest forest. Previously thought to be a fossil forest in upstate New York, it has since been realized that the world’s oldest forest is a lot further away.
Now that it has been discovered, researchers are trying to use the forest to decipher how trees were able to alter the planet and lead to human life as we know it.
Trees Have Existed for Millions of Years

Trees have been around on Earth for millions of years, making it quite difficult for scientists to discover where the oldest trees are. However, what is known is that trees were around before dinosaurs walked the Earth.
This helped life thrive on Earth, especially as trees give out oxygen. The arrival of the first forests enabled C02 levels to go down to modern levels, enabling life to start to form over time to get to where we are today.
The Gilboa Fossil Forest
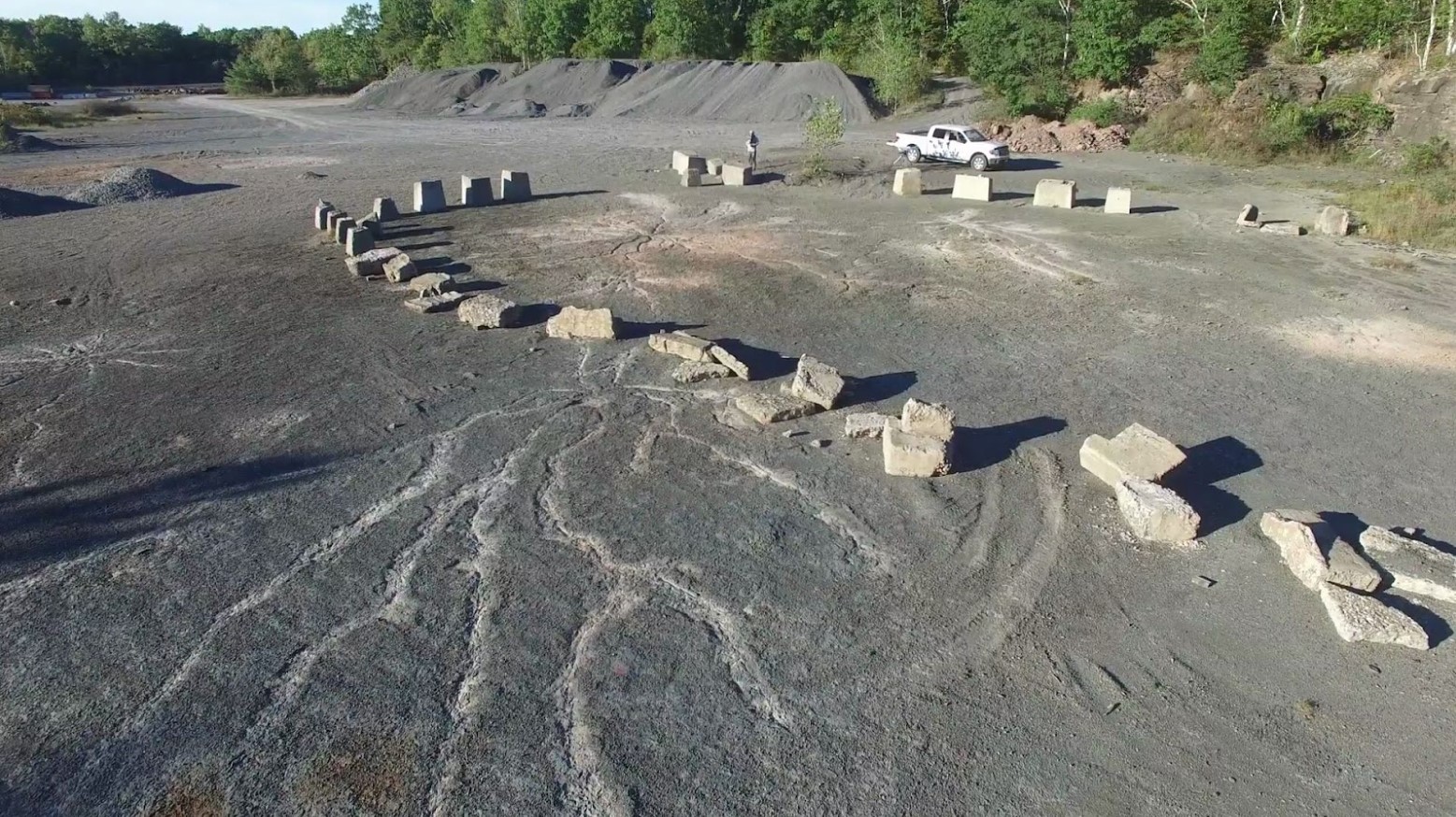

Before the latest discovery, the world’s oldest forest was believed to be the Gilboa fossil forest. Scientists discovered it in 2009 in an abandoned quarry in Cairo, New York.
Many might question how scientists can tell what the oldest forest is. With the Gilboa forest, they were able to tell because there were fossilized remains of Archaeopteris, which is an ancient plant featured within a rotted wooden system that has branches with leaves on. This tends to be found in 386-million-year-old rocks.
World’s Oldest Forest in South West England
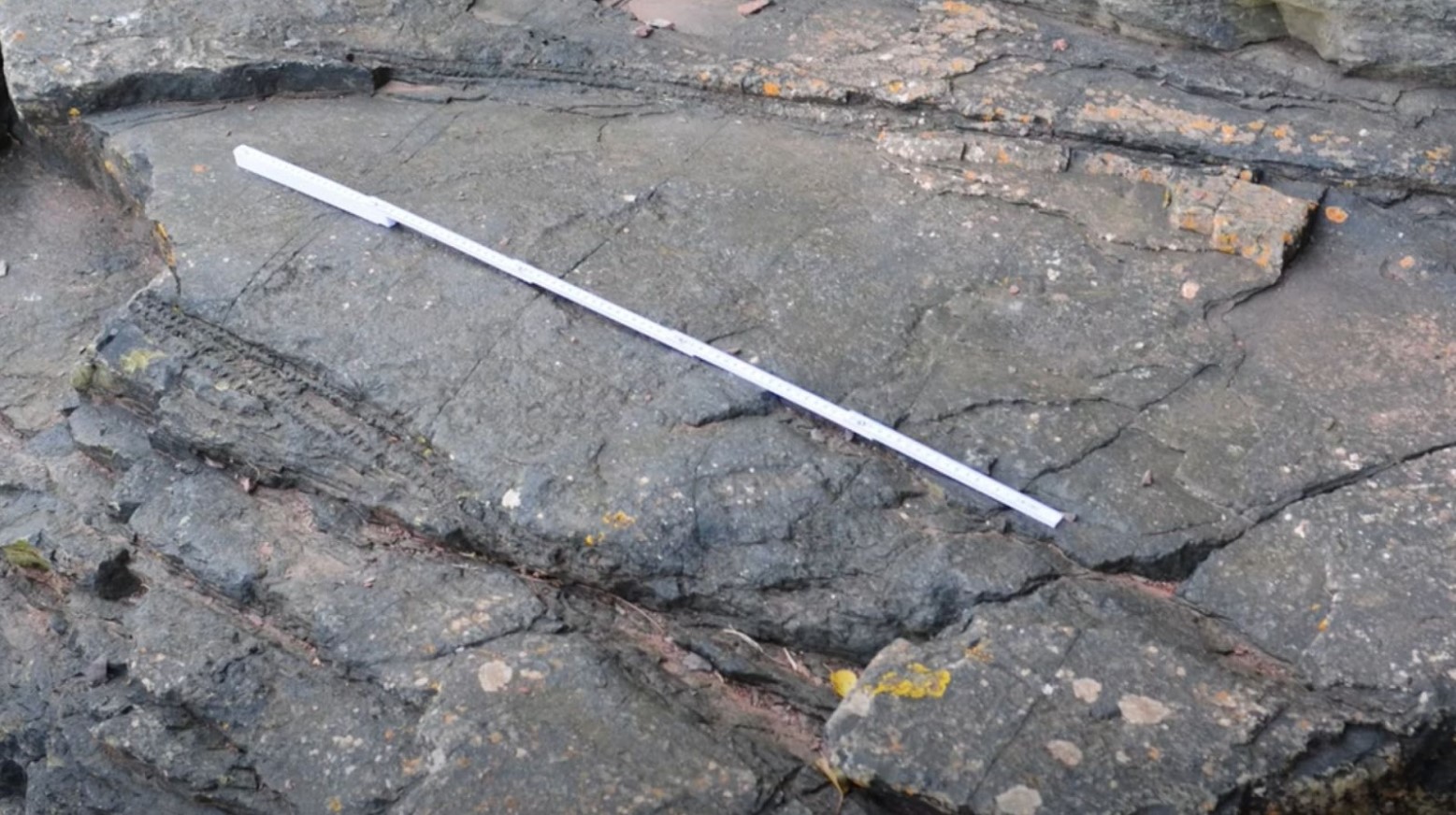

Since then, researchers have come across another forest that has since been found to be the oldest one in the world. This forest is in South West England, along the cliffs of Devon and the Somerset coast.
The forest is believed to date back to 390 million years ago (four million years older than the New York one), which they know because they were able to find fossils dating from back then that give evidence to it. Not only is it the oldest forest in Britain, but it is also the oldest on Earth.
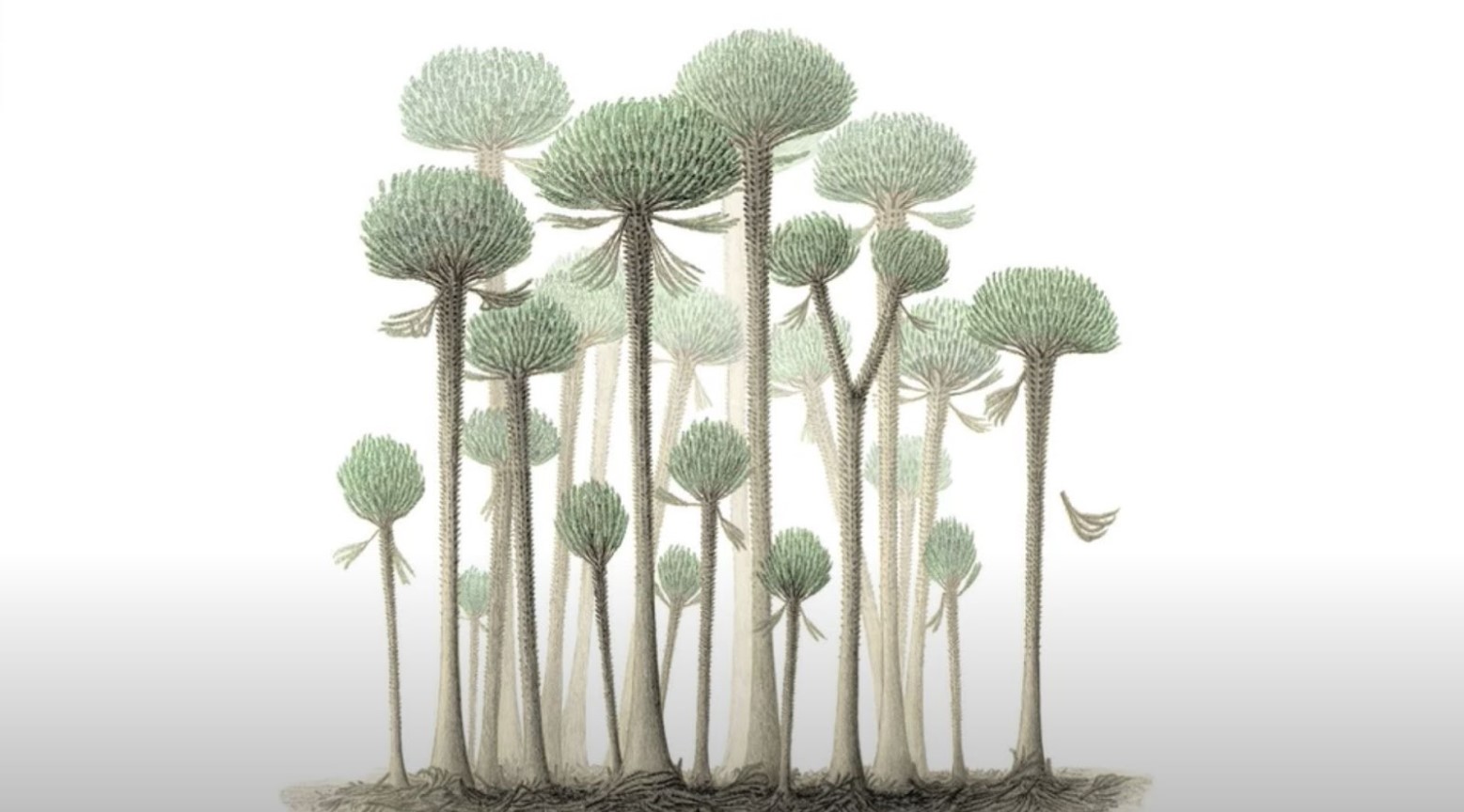
The Trees Are Calamophyton
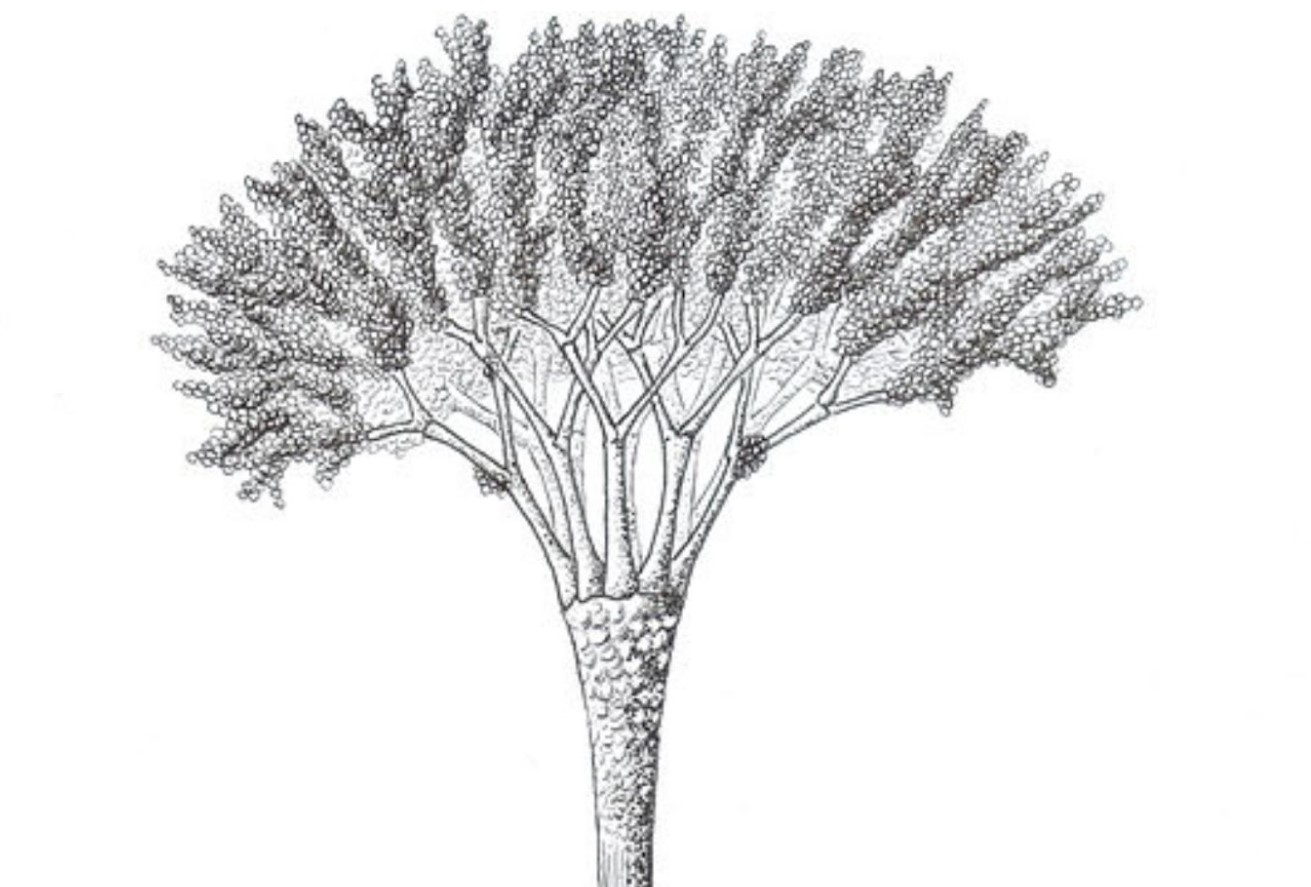
The fossilized trees in this forest are known as Calamophyton. When first seen, they tend to look like palm trees. Instead of being made from solid wood, the trunks were thin with a hollow center.
These trees didn’t tend to have any leaves, so the branches were covered in twig-like structures. They were a lot shorter than the ones that came before them, and when they grew, they shed their branches. As vegetation litter was on the floor, this would help the invertebrates on the forest floor.
The Bases of the Trees

The scientists also found evidence for the bases of the trees and their fallen trunks. These demonstrate what the environmental context and spacing between the trees would have been like when they were alive.
From this, they could tell what kind of environment the trees were growing in. It is believed they were next to a raised bank next to a small river channel.
The Devonian Period
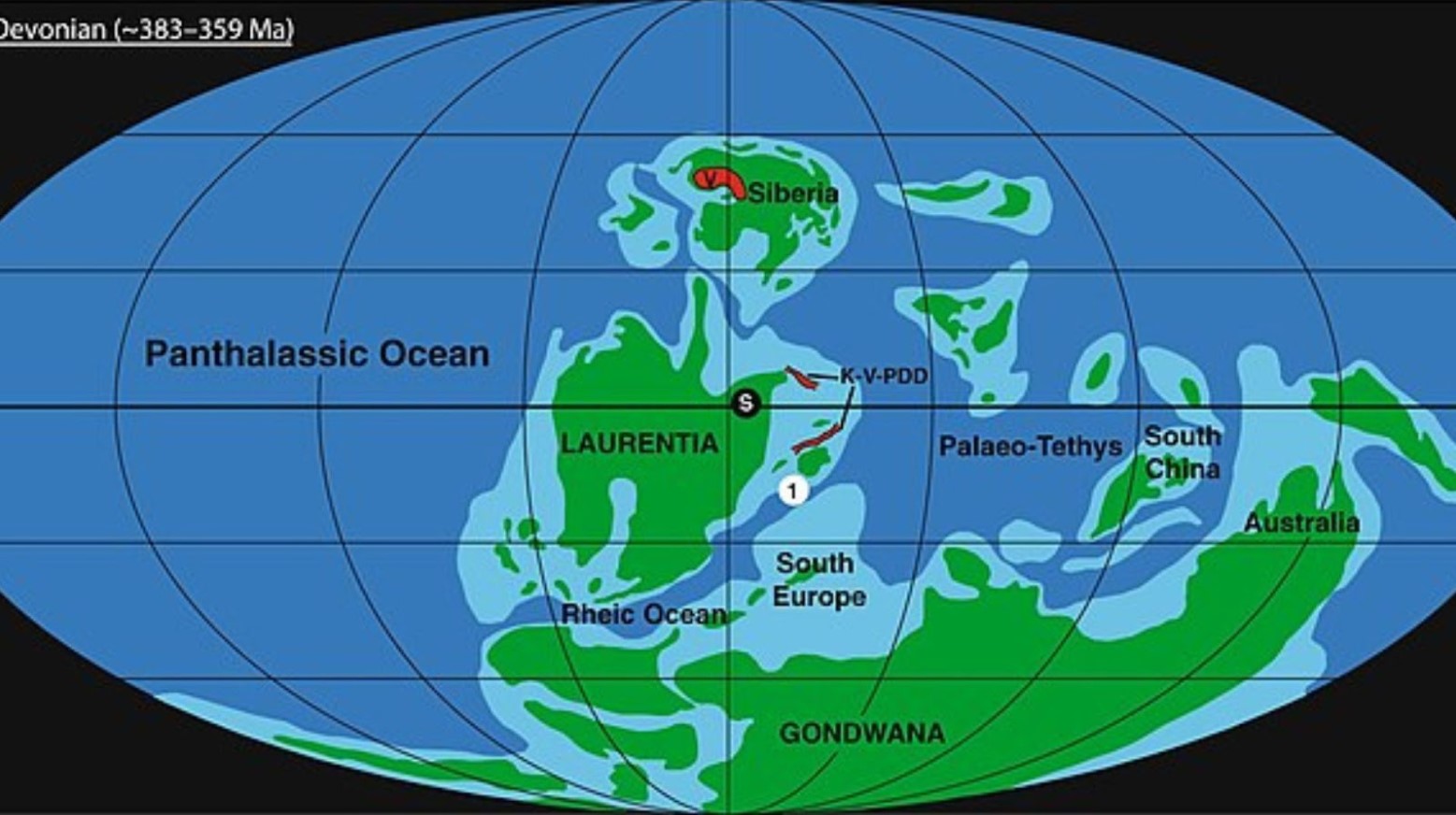
The trees are believed to have existed during the Devonian Period. When they first started growing, they formed a forest, helping to change the Earth’s land biosphere, impacting physical environments and stabilizing sediments.
Findings from the study provided evidence that the Eifelian Stage was the point where tree-driven changes to physical environments led to life as we know it, changing non-marine landscapes and the biosphere.
How Earth Was Able to Expand
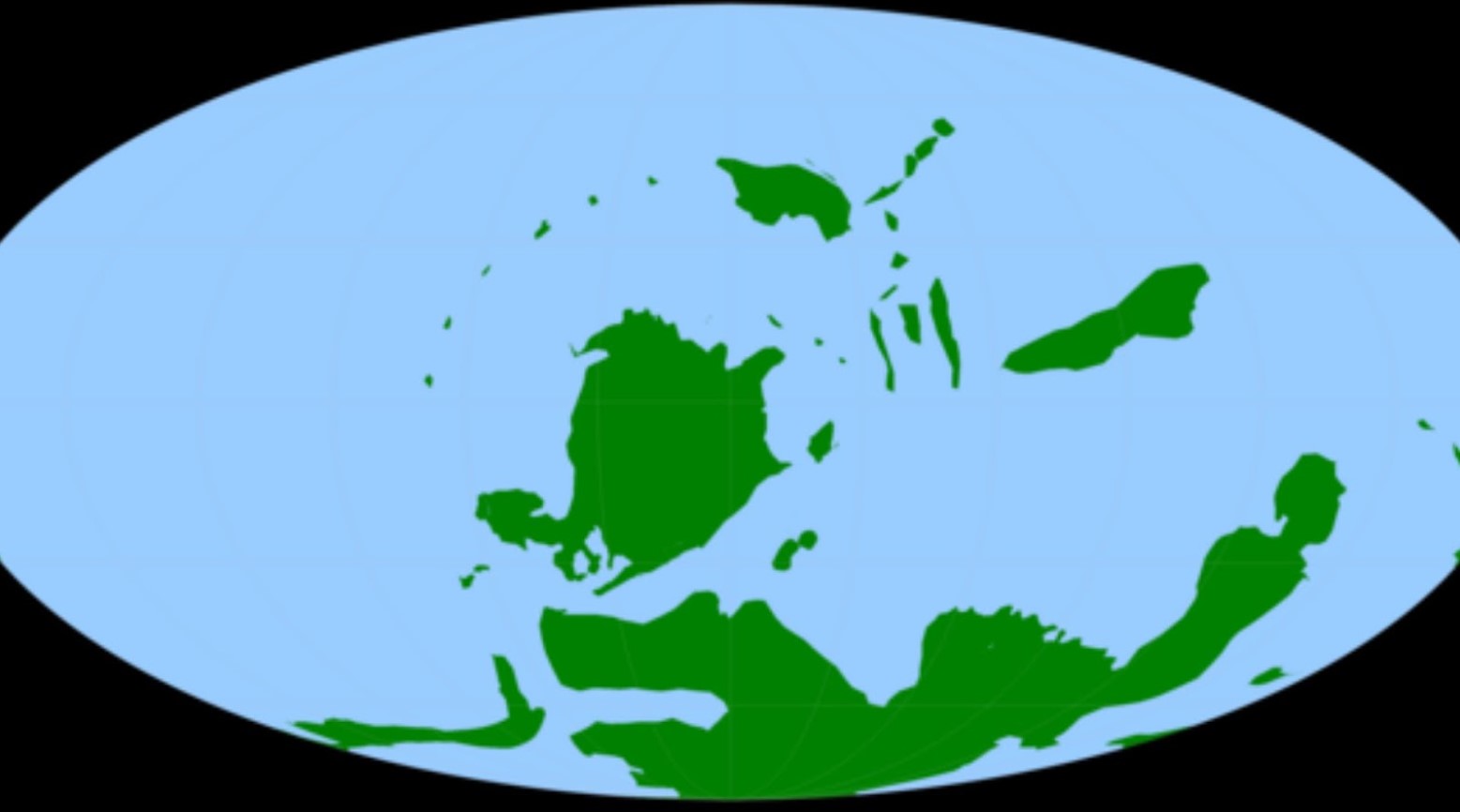
During the Devonian Period, the Earth expanded in ways it hadn’t previously. Plants started growing beyond wetlands, enabling inland forests to form with more robust wooden structures.
It also led to land animals, especially arthropods, moving to drier areas of the Earth when they had previously lived around the wetter areas.
A Surprising Discovery
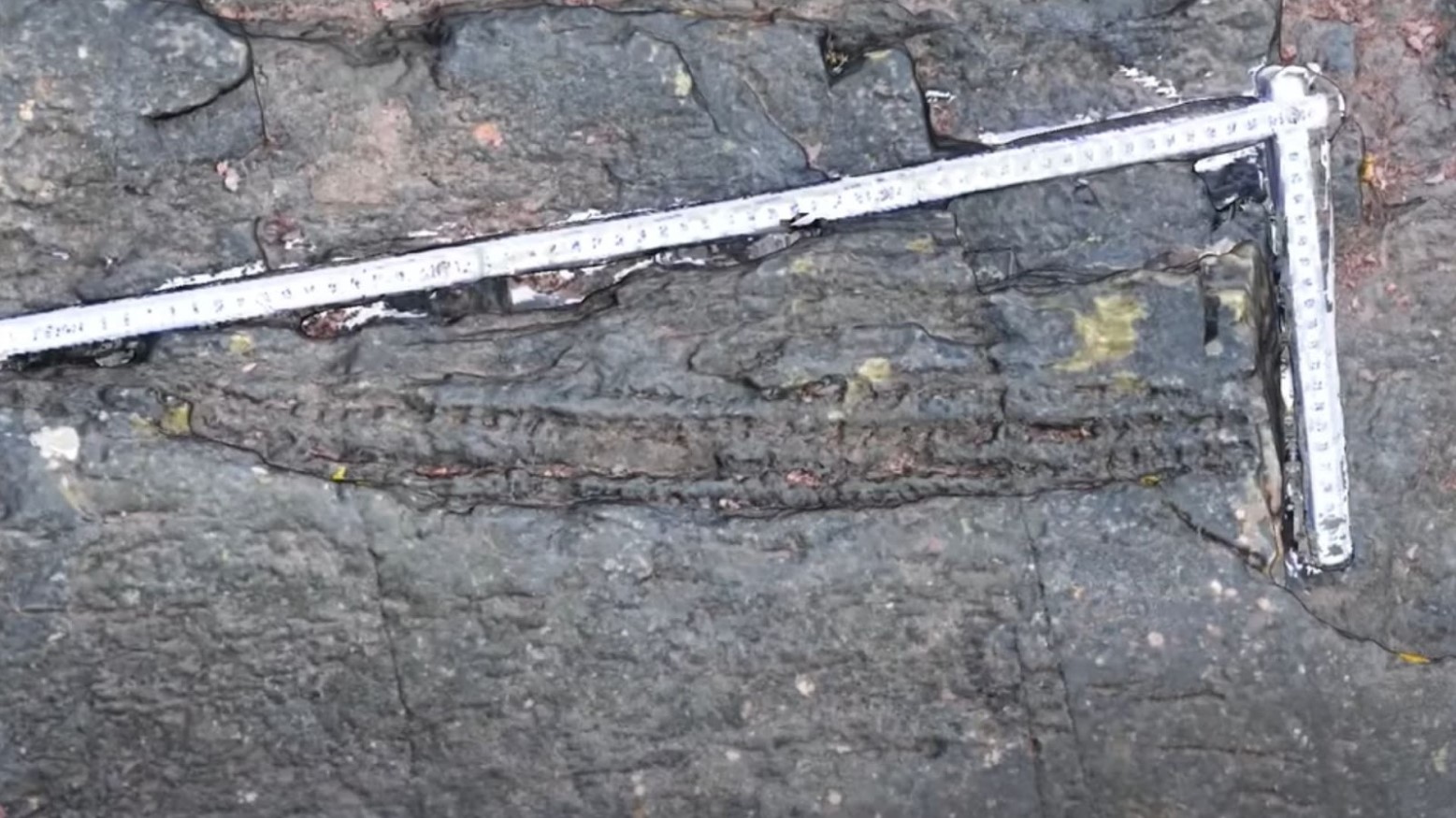

Dr Paul Kenrick, an expert in plant fossils at the Natural History Museum, said that he was surprised to find that there were fossils along the Devon and Somerset coasts, saying that he and the other researchers had no idea of a fossil forest of that age in the UK.
What was even more surprising was that they found the fossils inside rocks that weren’t previously thought to contain much fossil material.
Representing a Missing Part of History

While it is an amazing discovery to find the world’s oldest forest, it also represents a missing part of history in the area. This helps put the pieces together of how various life forms were formed on Earth.
What makes it even more impressive is that the area of fossilized rocks was very limited and difficult to access, so even getting a few samples is remarkable.
How Belgium and Germany Were Involved
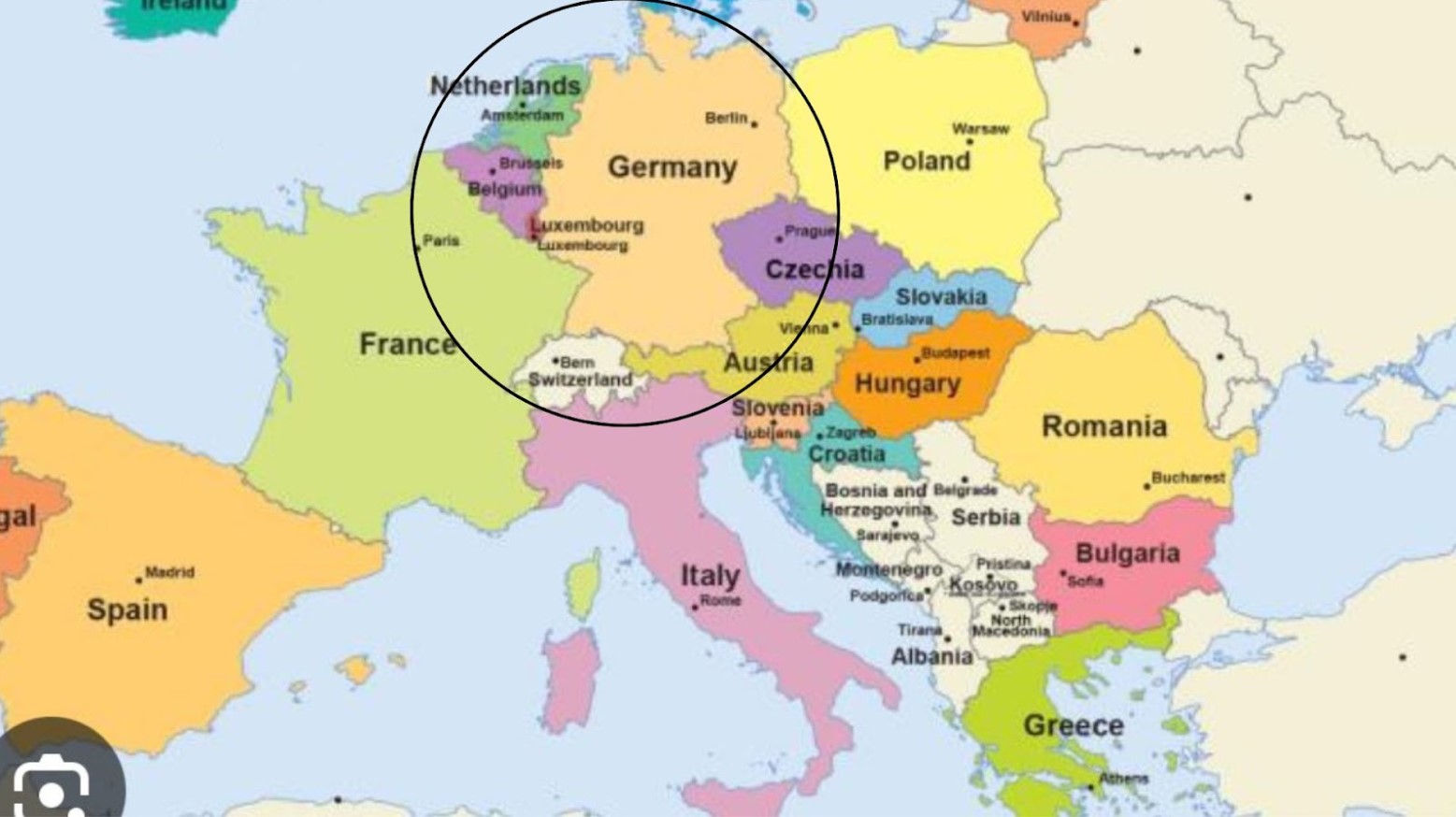
The world that existed millions of years ago didn’t look like the one we live in now. For starters, some countries and continents were a lot closer together and often went by different names.
During the Devonian Period, what is now known as the UK was much closer to mainland Europe, especially Belgium and Germany. The researchers believe the world’s oldest forest would have been much closer to these two countries during this era.
The Study of Earth’s Development

Having the world’s oldest forest in your country is a way to discover more about that immediate area’s history, as well as the history of the rest of the world.
Studying fossils of any kind helps us learn more about the history of the Earth and how humans, animals and nature have evolved over time. We learn new things about all of this every day, and new and interesting developments come up all the time, helping to confirm or challenge previously held beliefs.
