A new fossil study has revealed a stunning new fact about Homo floresiensis, the ancient human “Flores Hobbits” species, one of the smallest human species ever discovered.
New evidence has revealed that these hobbit-like species, which are related to modern humans, were even smaller than scientists initially thought. Now, they’re considered to be the smallest human ancestor species ever discovered.
The Discovery of the Flores Hobbits
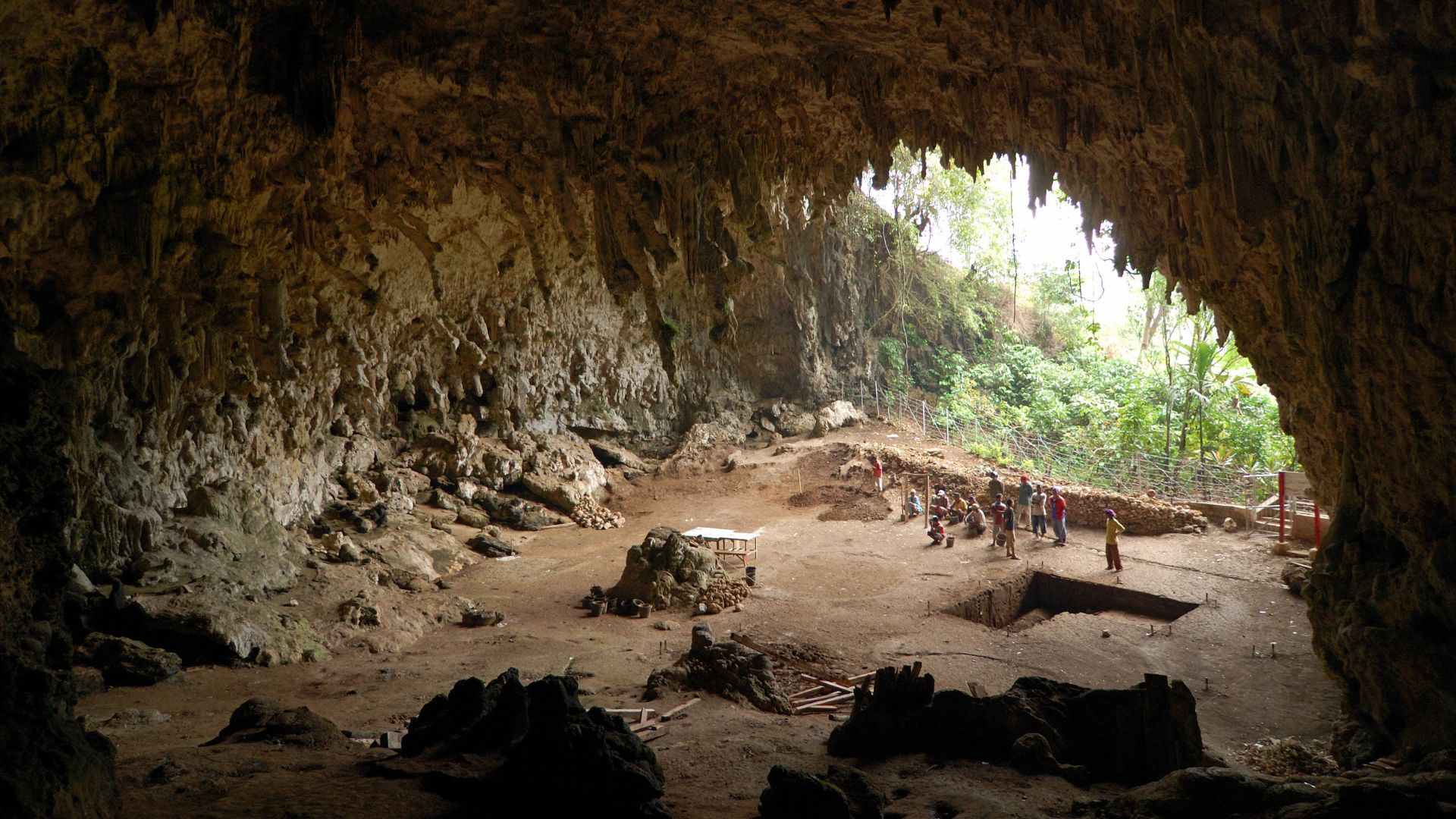

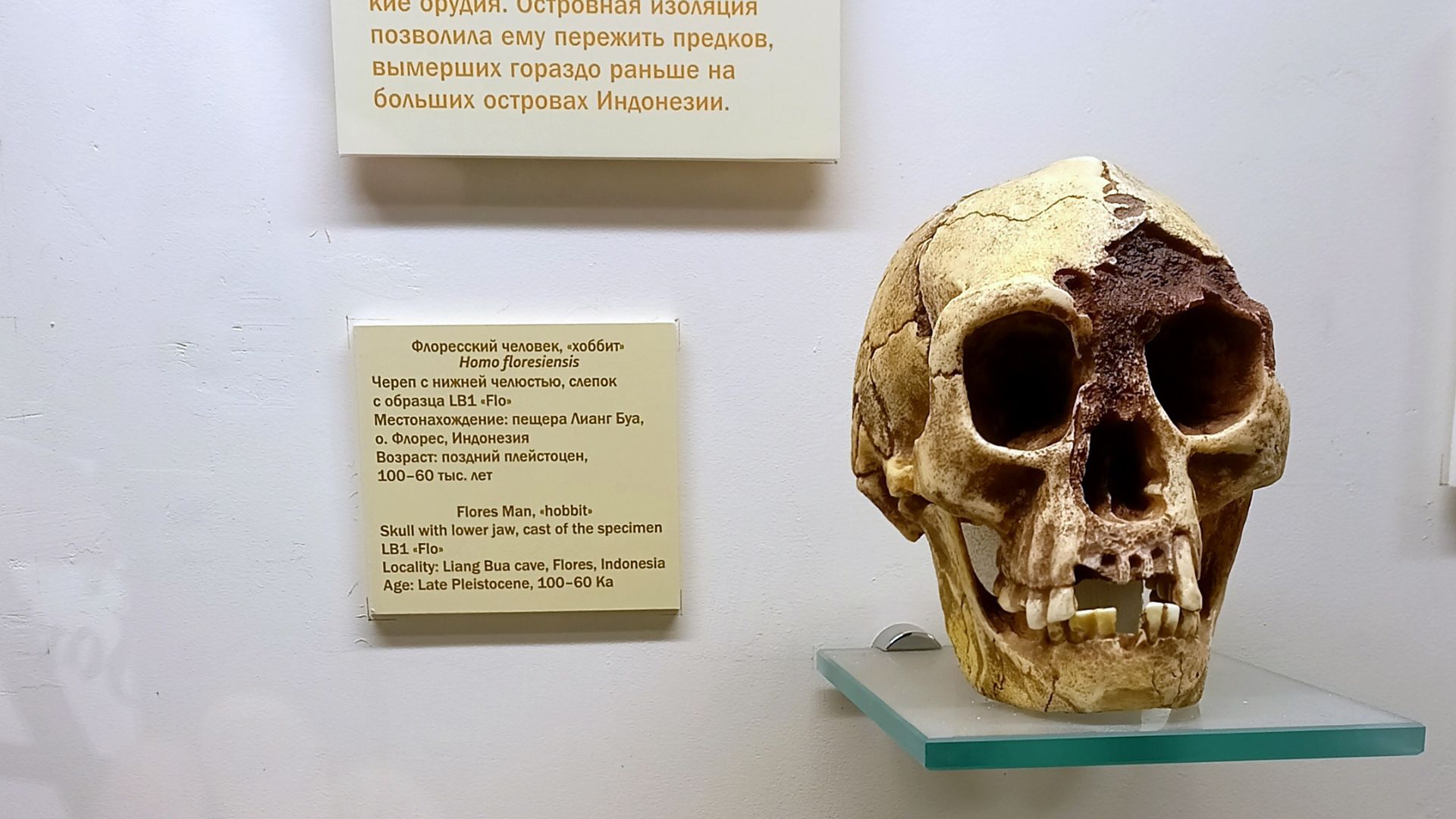
Archaeologists first became aware of the Flores Hobbits back in 2003 when the first fossils of the ancient human ancestors were discovered.
These bones were found on Flores, an Indonesian island, in the Liang Bua cave.
When These Hobbits Lived

According to scientists, this species lived on the Indonesian island as recently as 50,000 years ago.
At this time, Homo sapiens — our own modern-day human species — was living in Australia to the south of this cave. Therefore, both of these species were alive at the same time.
About This Small Species
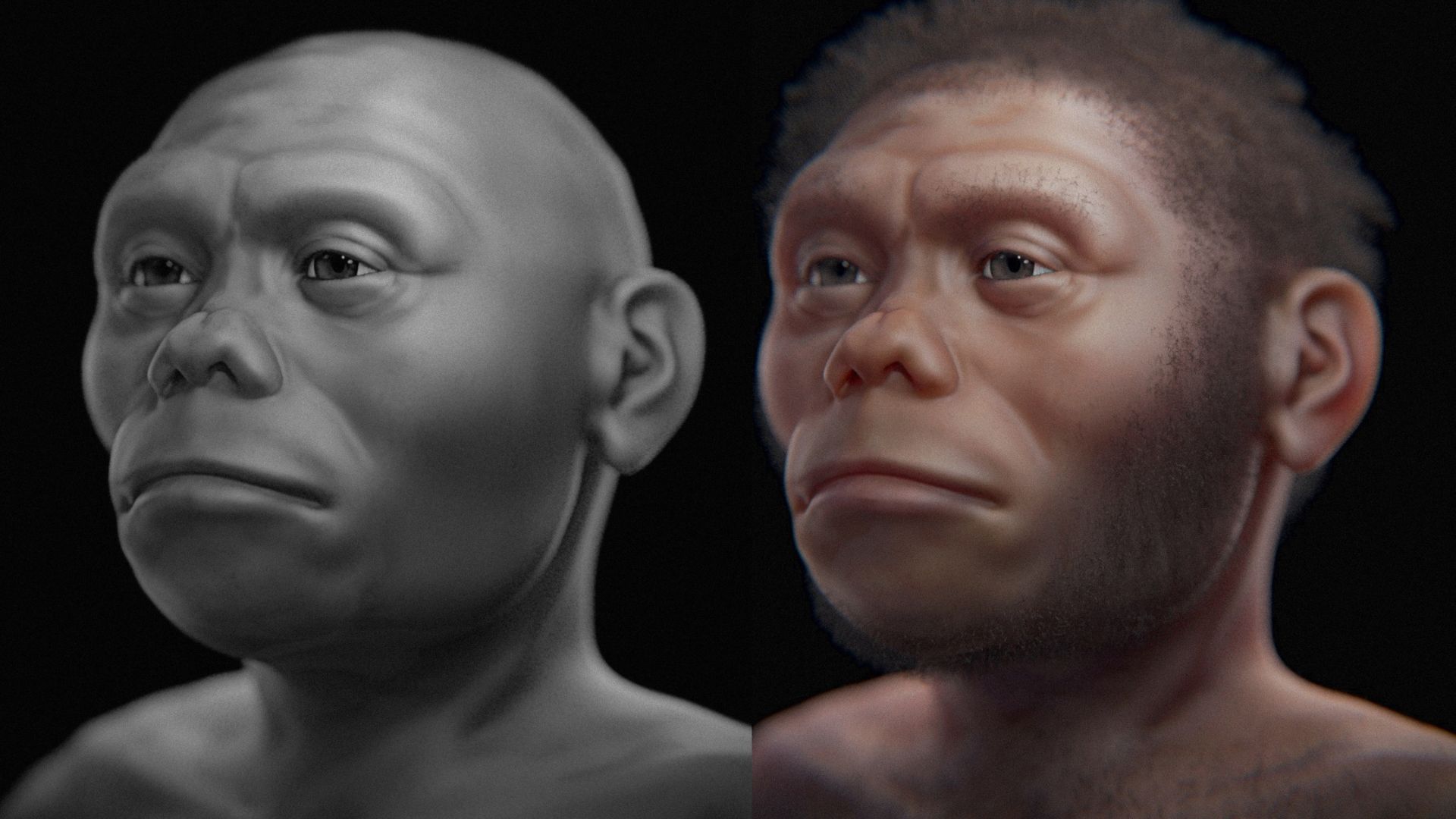

Once these rare bones were found, archaeologists got to work putting together a picture of what these small-brained people looked like.
Scientists soon found that these people had large teeth, even for their small size. They also only grew to about 3 feet 6 inches, making them an incredibly small species.
Initial Speculations About Homo Floresiensis
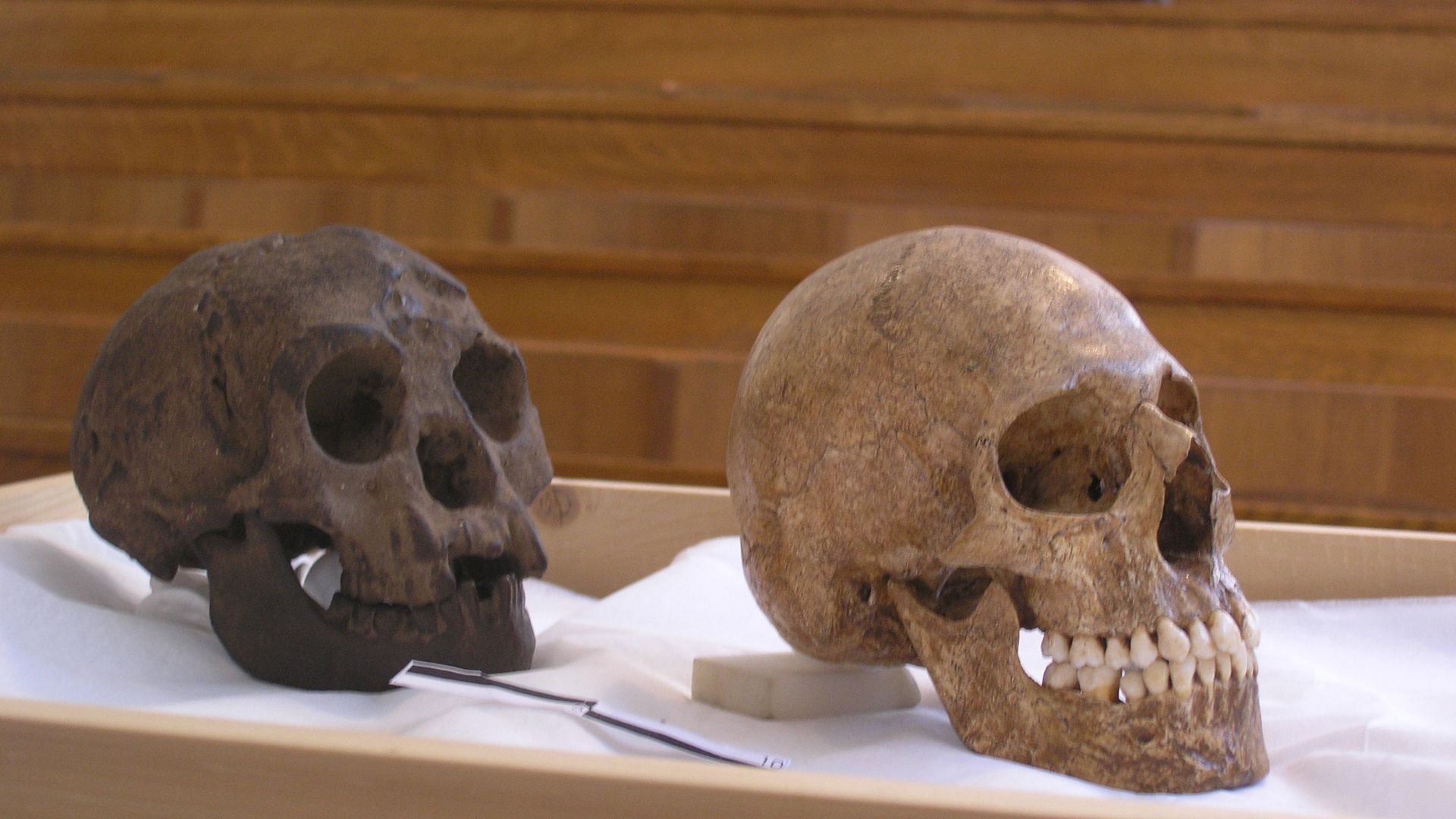

As there weren’t a ton of fossils and bones to go by, scientists had to speculate quite a lot about this ancient human ancestor.
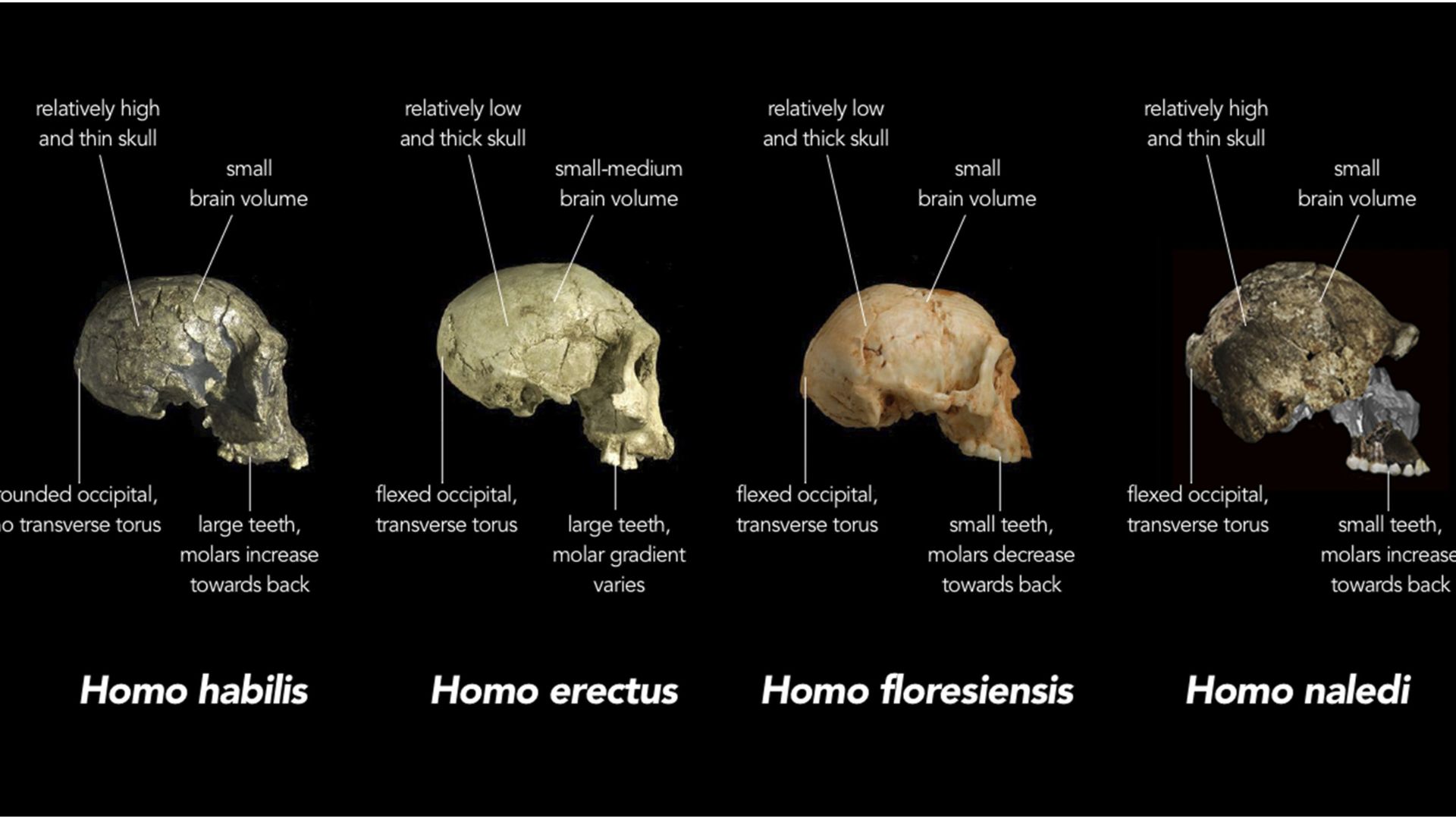
In general, scientists believed that Homo floresiensis was a descendant of Homo erectus, another human ancestor species. However, other speculations have also become prominent over the years.
The Ancestors of Homo Floresiensis
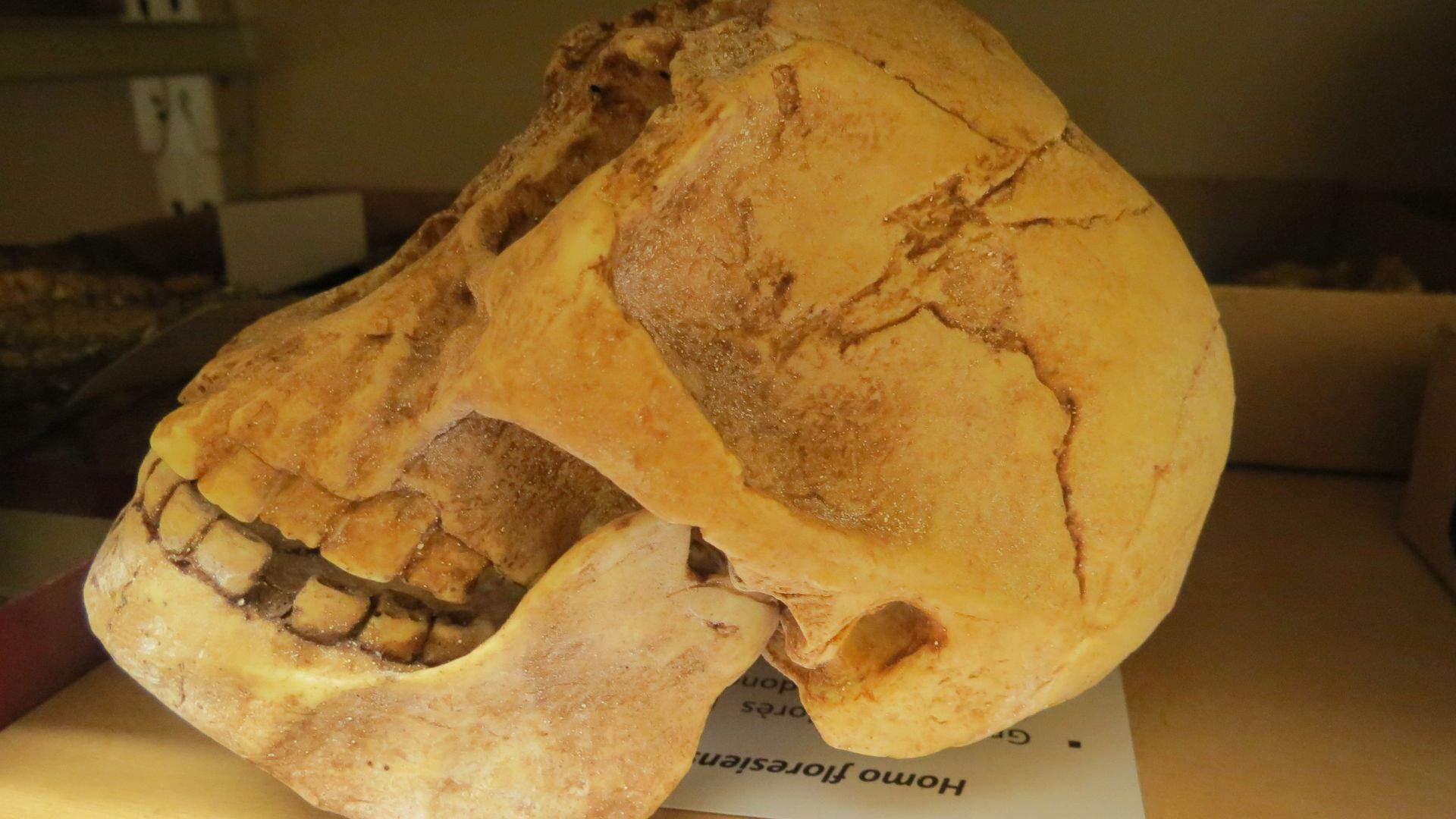

Another common theory speculated that this small species was the remnant of another ancient human ancestor species that predated Homo erectus.
This theory put forth that Homo floresiensis was a late surviving remnant of this older species from Africa. This ancestor species was also thought to be small in stature.
Other Fossil Discoveries
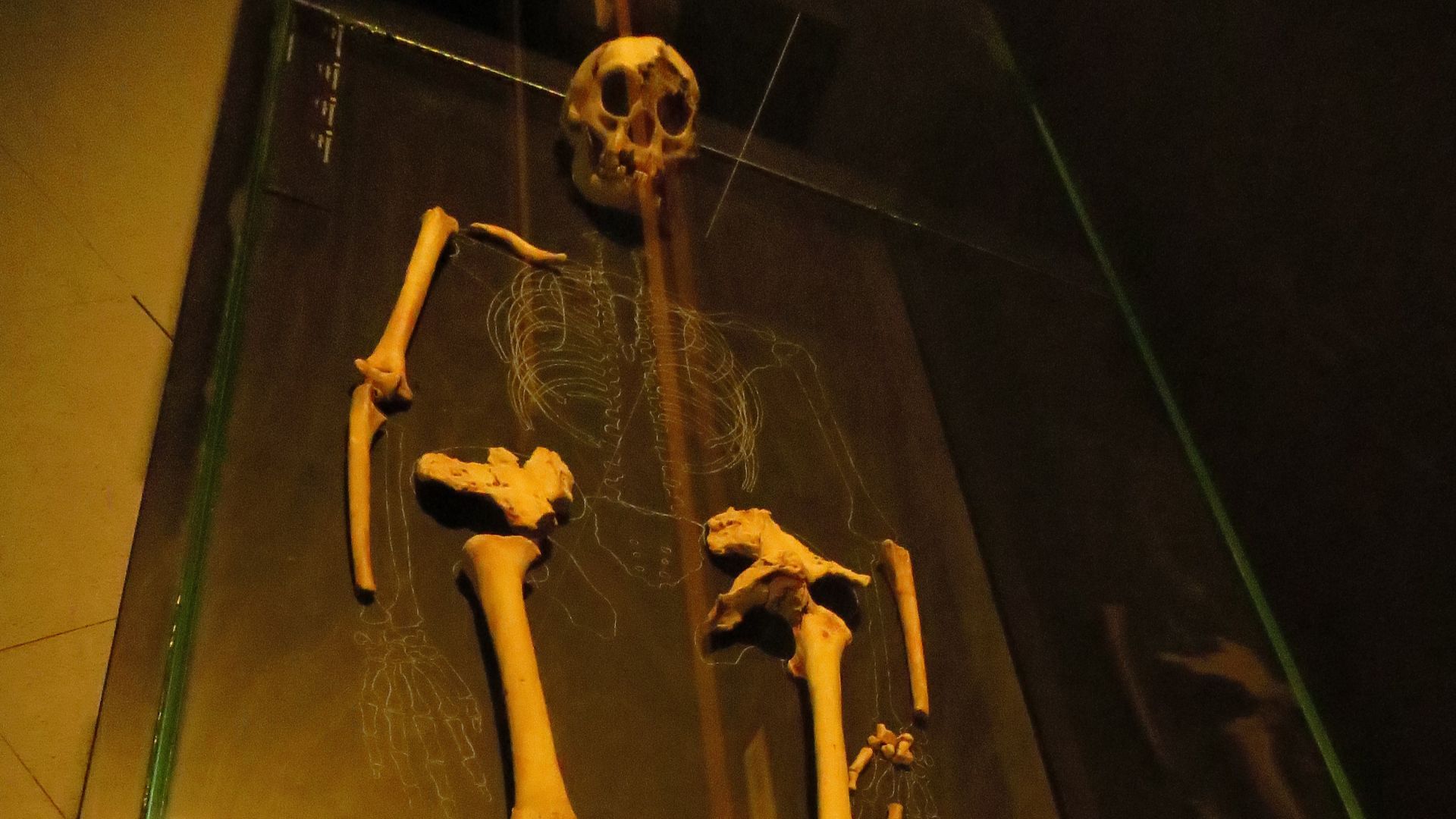

Previously, scientists also found small ancient human fossils on Flores, about 75km east of the Liang Bua cave where the Flores Hobbit fossils were first discovered.
Researchers found that these fossils were even smaller than the Homo floresiensis bones — and that they were older, from around 700,000 years ago.
New Fossil Finds

Now, new research has brought forth three more fossils from this new site, also from 700,000 years ago. Scientists believe that these bones show that the Flores Hobbits indeed come from a smaller-statured ancient human species.
These bones are much smaller than the other fossils found, which stunned researchers. They now believe that the Flores Hobbits and their ancestors were incredibly small.
Small Bones
Adam Brumm, the co-author of this study, explained how these bones were much shorter and smaller than the initial Homo floresiensis ones.
“This 700,000-year-old adult humerus is not just shorter than that of Homo floresiensis, it is the smallest upper arm bone known from the hominin fossil record worldwide,” Brumm stated.
A Smaller Species Than Initially Thought
These fossil discoveries have further changed how scientists think about the Flores Hobbits.
Brumm added, “This very rare specimen confirms our hypothesis that ancestors of Homo floresiensis were extremely small in body size. However, it is now apparent from the tiny proportions of this limb bone that the early progenitors of the ‘Hobbit’ were even smaller than we had previously thought.”
Small Human Species From the Past
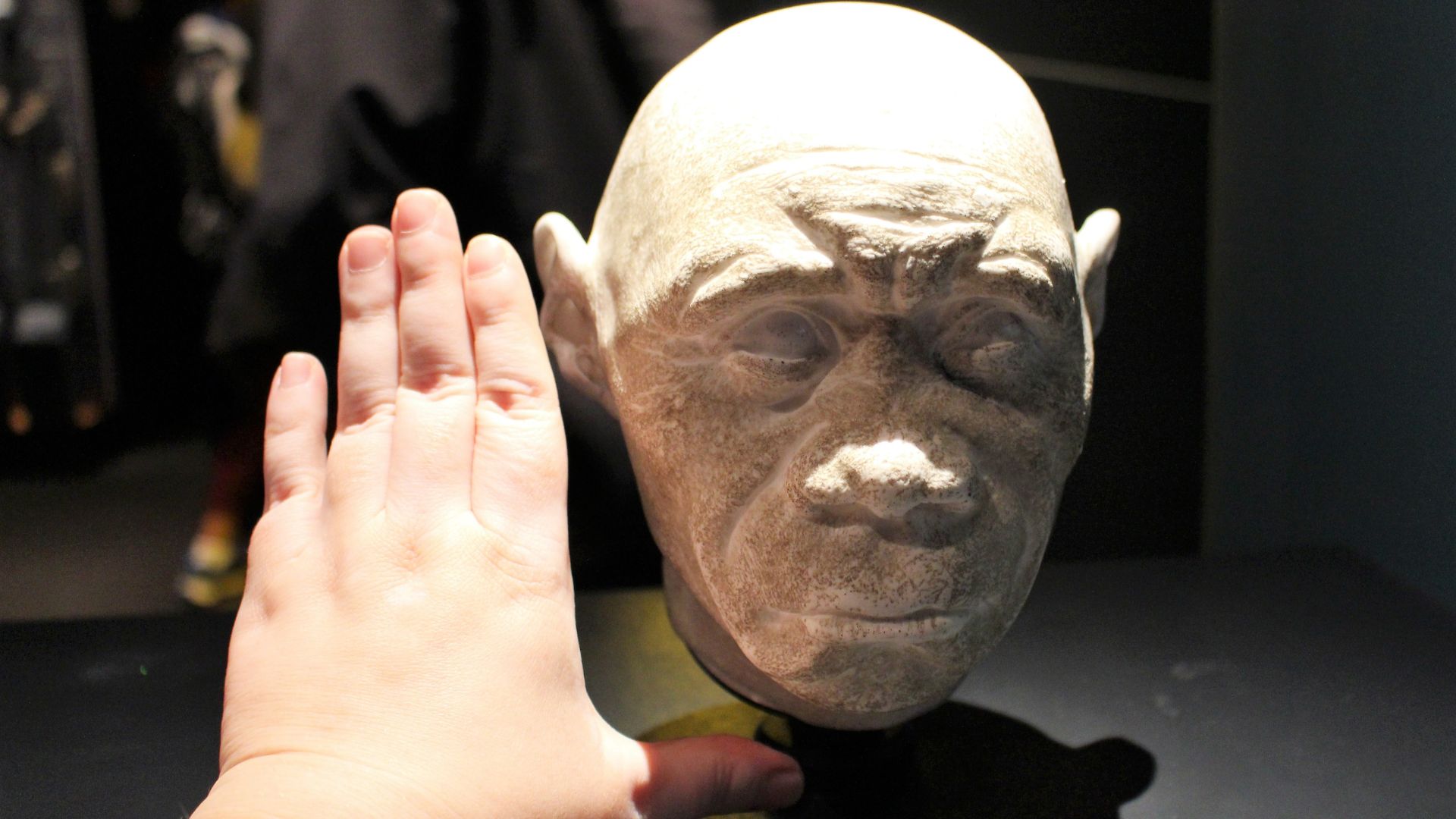

This new study further highlights how these new fossils were possibly “direct ancestors” of Homo floresiensis, or an “older variant.”
However, these ancestors were still different than the Flores Hobbits, as they didn’t have as many specialized teeth as them.
New Discoveries of Ancient Human Ancestors

This remarkable study further highlights how archaeologists are still uncovering new facts about various ancient human ancestors — ancestors that science wasn’t aware of for the last thousands of years.
As the first Homo floresiensis fossils weren’t even discovered until 2003, scientists may still have brand new discoveries to make about this interesting, small-statured species.
