The economic policies and growth trajectories of the United States and China are markedly diverging. This shift is reflected in their respective stock markets, highlighting different approaches and outcomes in their economies.
According to Business Insider, experts have analyzed the economic and market outlooks for these two superpowers, underscoring the contrast in their paths.
US Experiences Significant Growth

The United States has reported a robust quarter of economic growth, with real GDP reaching 3.3% in the last three months of 2023, surpassing expectations. This follows a remarkable 5% growth in the preceding quarter, challenging the recession narrative.
The International Monetary Fund has responded by raising its global GDP outlook from 2.9% to 3.1%, reflecting the strength of the US economy, Business Insider reports.
China Faces Economic Challenges

China, conversely, is encountering significant economic challenges as it emerges from pandemic lockdowns.
Issues such as mounting debt, deflation, and a troubled real estate market have led to a decrease in foreign investment in the country’s financial markets, according to Business Insider.
US-China Economic Imbalance

Arthur Laffer Jr., president of Laffer Tengler Investments, discussed with Business Insider the imbalance between the US and China, noting its impact on both nations.
He said, “A strong US economy buys more foreign goods from China with a stronger US dollar,” which helps sustain China’s manufacturing and exports. However, he also pointed out that China’s policy initiatives are more like “Band-Aids” that fail to address the root causes of its economic issues.
Xi Jinping’s Growth Ambitions

According to Business Insider, under President Xi Jinping’s leadership, China is striving to achieve its growth ambitions despite facing internal challenges and the external economic strength of its biggest rival, the United States.
This situation places Beijing in a delicate position as it navigates through its domestic issues and the comparative economic performance of the US.
Diverging Consumer Bases

Joseph Seydl, a senior markets economist at JPMorgan Private Bank, highlighted to Business Insider the stark differences between the consumer bases in the US and China.
The US has seen strong consumer spending, aided by pandemic stimulus checks and unemployment benefits, in contrast to China, where policymakers have been more cautious, focusing on export growth over domestic consumption.
Stimulus Measures in the US and China
The approach to stimulus measures varies greatly between the US and China, reflecting their differing economic strategies. The US has actively supported its population through financial aid, which has helped maintain consumer spending and economic momentum, as per Business Insider.
In contrast, China has prioritized export growth, wary of stimulating domestic consumption too much for fear of affecting exports or causing inflation.
The Real Estate Sector in China

China’s real estate market is currently facing significant challenges, with efforts to deleverage and reduce risks.
The downturn in this sector has had a substantial impact on consumer sentiment and spending, as a large portion of Chinese citizens’ wealth is tied to real estate. Business Insider reports that tumbling property values have led to decreased confidence and increased savings among consumers.
Liquidation of China Evergrande

A Hong Kong court ordered the liquidation of China Evergrande, the world’s most indebted real estate developer, as reported by Business Insider.
This development complicates the government’s efforts to support the sector and affects over a million people who have paid for homes that have not been built, highlighting the severe challenges in China’s real estate market.
US Real Estate Market Faces Different Challenges

The real estate market in the US, both commercial and residential, faces its own set of challenges, albeit not as severe as those in China.
Business Insider reports that high interest rates have affected home buying activity, and the shift towards work-from-home trends has impacted the commercial market. However, experts do not foresee these issues as a systemic threat to the US economy.
Stock Market Performance Reflects Economic Fortunes

The differing economic fortunes of the US and China are evident in their stock market performances.
US stocks have seen significant gains, whereas Chinese and Hong Kong stocks have experienced a sharp decline, reflecting the exodus of foreign investors and the underperformance of China’s benchmark indexes compared to those of the US and other large economies, as per Business Insider.
Market Predictions for 2024
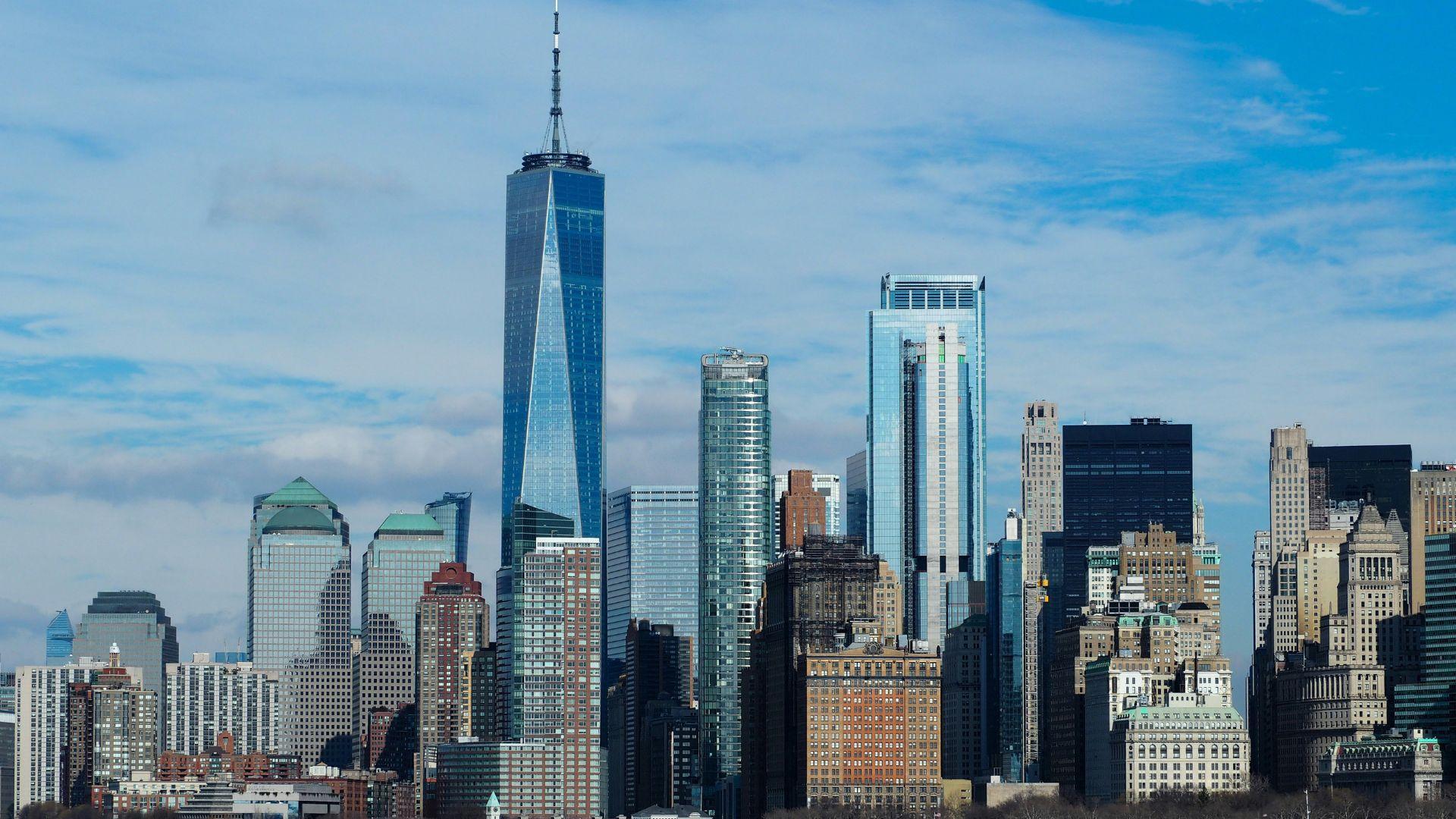

Market analysts predict that the disparity between the American and Chinese stock markets may narrow in 2024.
Laffer Jr., told Business Insider “I expect that the Chinese market will bounce around, but that the bias is towards more pain since the problems are systemic, in my opinion. The US, on the other hand, should do well for the 2024 period — strong economy, strong employment, strong earnings, strong dollar.”
China’s Rapid Rise

According to data from the World Bank, China’s GDP increased by an average of 9 percent per year since it opened up its economy in 1978.
Between 2000 and 2021, the size of the Chinese economy grew tenfold. In the year 2000, China had a $1.2 trillion economy and in 2021 it had grown to almost $18 trillion.
China’s Growing Pains

Some economists are placing the blame on China’s recent economic struggles as the consequences of its rapid economic expansion that was continually pushed by the government at great cost.
According to Econofact, China owes its growth to market reforms and globalization. However, this reliance on the global economy guaranteed that it was bound to come to a halt with an event like the COVID-19 pandemic.
How Bad is the Debt?

Bloomberg reported in January that China’s debt-to-GDP ratio has reached a record high. In the fourth quarter of 2023, this ratio reached 286.1%.
This is at a ratio in 2023 that even exceeds the debt ratio of the United States, which reached 124.2% in December 2023 according to CEIC Data. This debt has been exasperated by overbuilding and overdevelopment of real estate in the country.
China’s Debt is Owned by the State

According to Reuters, China’s debt crisis can be blamed on many of the state-owned firms in the country.
The country’s leadership was keen to keep economic growth going ahead at breakneck speeds, which resulted in many companies continually taking out debt to fund the expansion. Now these Chinese companies are unable to make their debt payments as the economy is starting to stall.
The Health of Chinese Companies

A data analysis by Reuters found that the number of mid-to-large-sized companies with a healthy amount of debt fell drastically in just 8 years.
In 2008 the number of companies with healthy levels of debt they could pay back was 845. Just a short time later in 2016, that number had dropped to 577, representing a 31.7% decrease.
Companies With Unhealthy Debt Quickly Grew

The Reuters analysis also found that the number of larger debt-holding companies, with an unhealthy debt ratio, ballooned during the same time.
In 2008, only 262 of these companies had an unhealthy level of debt. This number changed to 395 in just 8 years. The data suggests that two-thirds of corporate debt in the country belongs to Chinese state-owned companies.
The Pandemic’s Effect On China

According to the China Research Center, the pandemic was one of the major contributors to the country’s recent economic downturn.
They also place blame on the 2018 trade war and the real estate decline of 2021. In response to the outbreak of COVID-19 China instituted harsh public health protocols that severely affected the country’s economy, causing it to slow tremendously.
China’s Public Health Policies

China Research Center estimates that there were hundreds of cases of COVID-19 initially discovered in December 2019 in Wuhan, China.
The country became the epicenter of the pandemic and decided to launch a Level 1 Provincial Response to Public Health Emergency. This is the highest level of response and requires not just patients but suspected patients and any close contacts to be held in quarantine.
The Cases Didn’t Stop
Despite China’s “Zero-Covid” health policy measures, the virus continued to spread to other areas of the country. The country implemented harsh measures that included preventing people from leaving high-risk areas.
According to Chinese Research Center, political pressure eventually forced them to halt these measures, but another spike in cases in 2022 further depressed the economy. It wasn’t until 2023, nearly three years later, that China could begin to recover.
End of the China Miracle

China’s economic growth is often referred to by economists as the ‘China miracle’ because of how high the growth was and how long it was sustained.
This growth suddenly halted after the outbreak of COVID-19, according to Chinese Research Center. Economic growth went from 6% per year in 2019 to just 2% in 2020.
China Can’t Spend Its Way Out

According to Chinese Research Center, analysts think that the current rate of domestic consumption is too low to sustain the current Chinese economy.
This leaves the economy dependent on public investment from the government to rekindle and stimulate growth. However, a heavy-handed investment approach has its downsides. Mainly it hurts productivity which will further hinder the recovery.
China Diverging from the United States

When the United States had its own financial crisis in 2008, it resulted in an unprecedented public spending stimulus package in the country’s history.
According to Business Insider, the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 delivered $831 billion in aid to jumpstart the economy. China so far has been resistant to a stimulus approach to economic recovery, taking lessons from the American experience and hoping to avoid more ballooning debt.
